What Molecule Does a Sequence of Dna Typically Code for
Usually the insert is the interesting part consequently. Even within a gene only some sequences called exons code for.
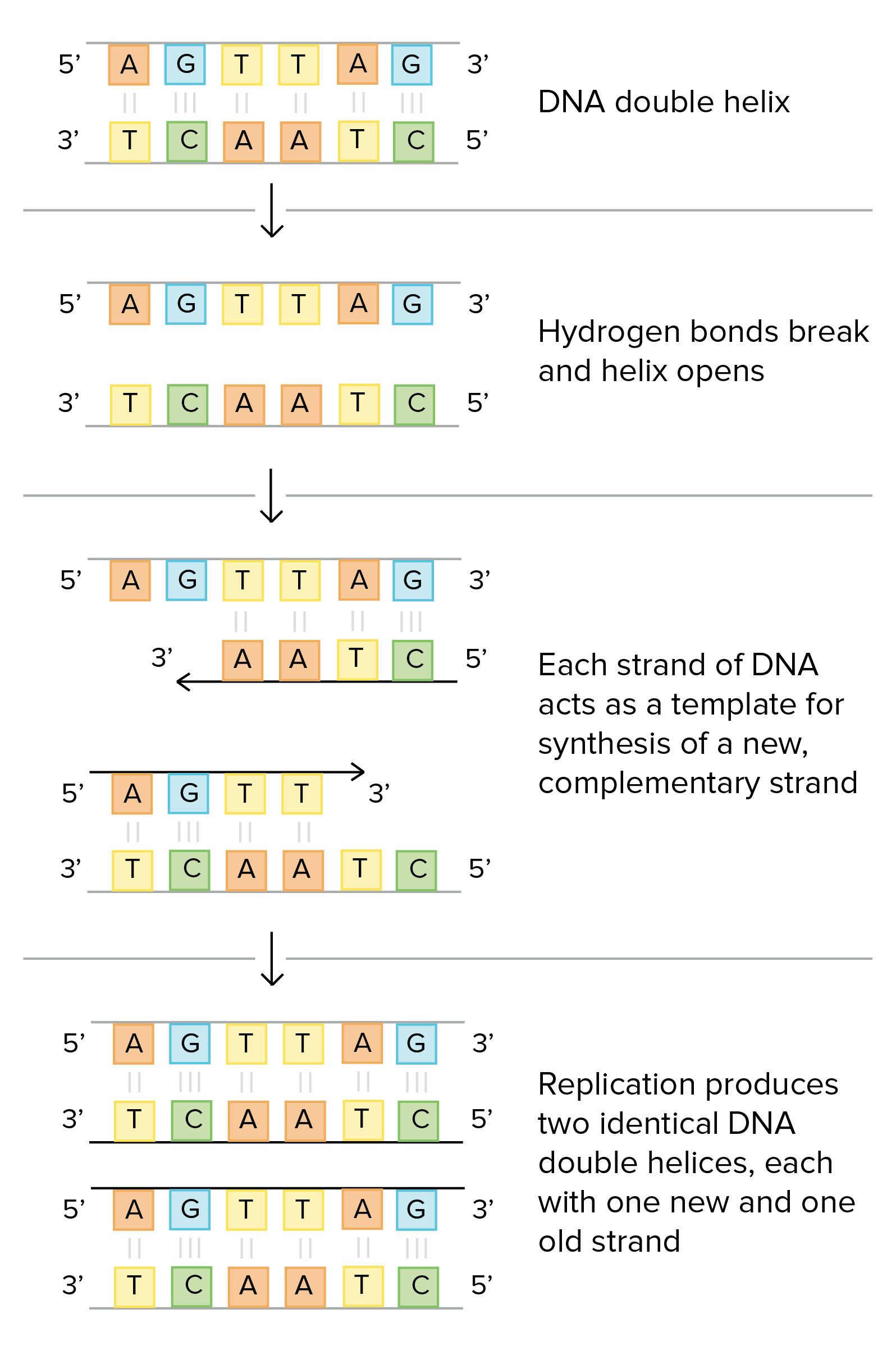
In DNA the code letters are A T G and C which stand for the chemicals adenine thymine guanine and cytosine respectively.
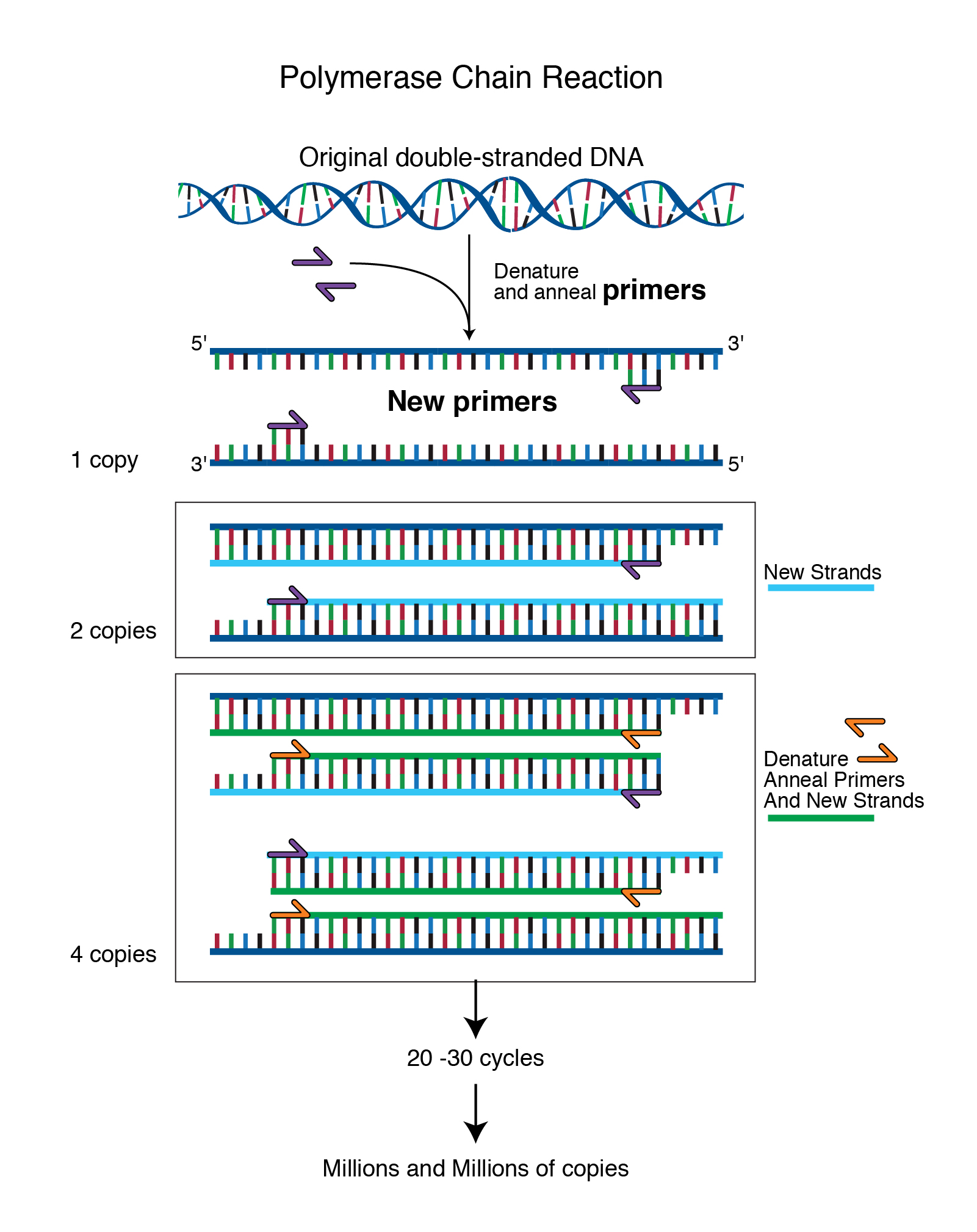
. Insert The insert is a piece of DNA weve purposely put into another a vector so that we can replicate it. B the redundancy of the genetic code. In eukaryotes much of the nuclear DNA does not code for polypeptides.
The vector is generally the basic type of DNA molecule used to replicate your DNA like a plasmid or a BAC. Both of these codons code for proline. What molecule does a sequence of DNA typically code for.
Sequencing DNA means determining the order of the four chemical building blocks - called bases - that make up the DNA molecule. Coding regions called exons which specify a sequence of amino acids. It consists of a specific sequence of nucleotides at a given position on a given chromosome that codes for a specific protein or in some cases an RNA molecule.
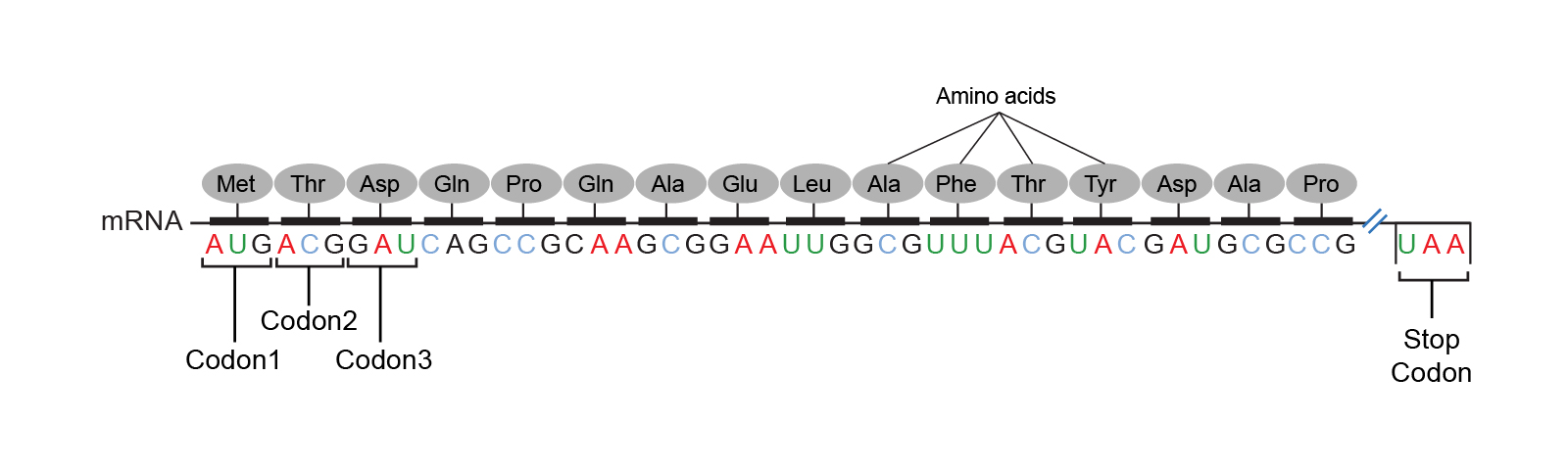
Each set of 3 nucleotide is called as codon and each codon encode an amino acid during translation process. Genes consist of three types of nucleotide sequence. In base pairing adenine always pairs with thymine and guanine always pairs with cytosine.
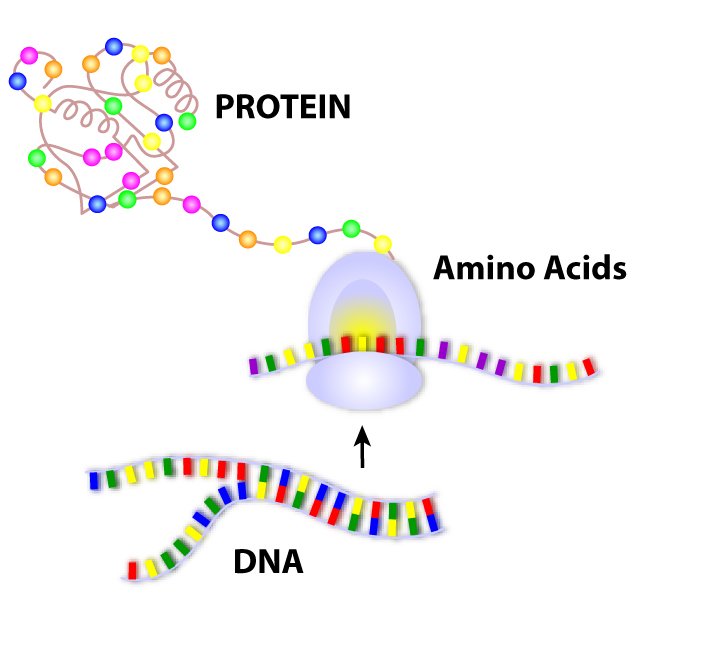
In a molecule of double-stranded DNA the amount of Adenine present is always equal to the amount of. The amino acids will then form a chain in the sequence of the DNA nucleotide sequence. DNA is composed of series of molecules called as nucleotide.
The genetic code is universal non-overlapping and degenerate. There are for example non-coding multiple repeats of base sequences between genes. A sequence of three DNA bases called a triplet codes for a specific amino acid.
One may also ask what is the importance of the sequence of nucleotides in genetic information. There are 4 nitrogenous bases that compose DNA nucleotide Adenine Guanine Cytosine Thymine. Imagine that a mutation in a DNA molecule results in the codon CCU being changed to CCC.
These amino acids are the building blocks of protein. The DNA nucleotides codes for codons on an mRNA strand in transcription the codons will then pair with a tRNA molecule that holds an amino acid. What molecule does a sequence of DNA typically code for.
April 09 2016 021101 AM. The sequence tells scientists the kind of genetic information that is carried in a particular DNA segment.
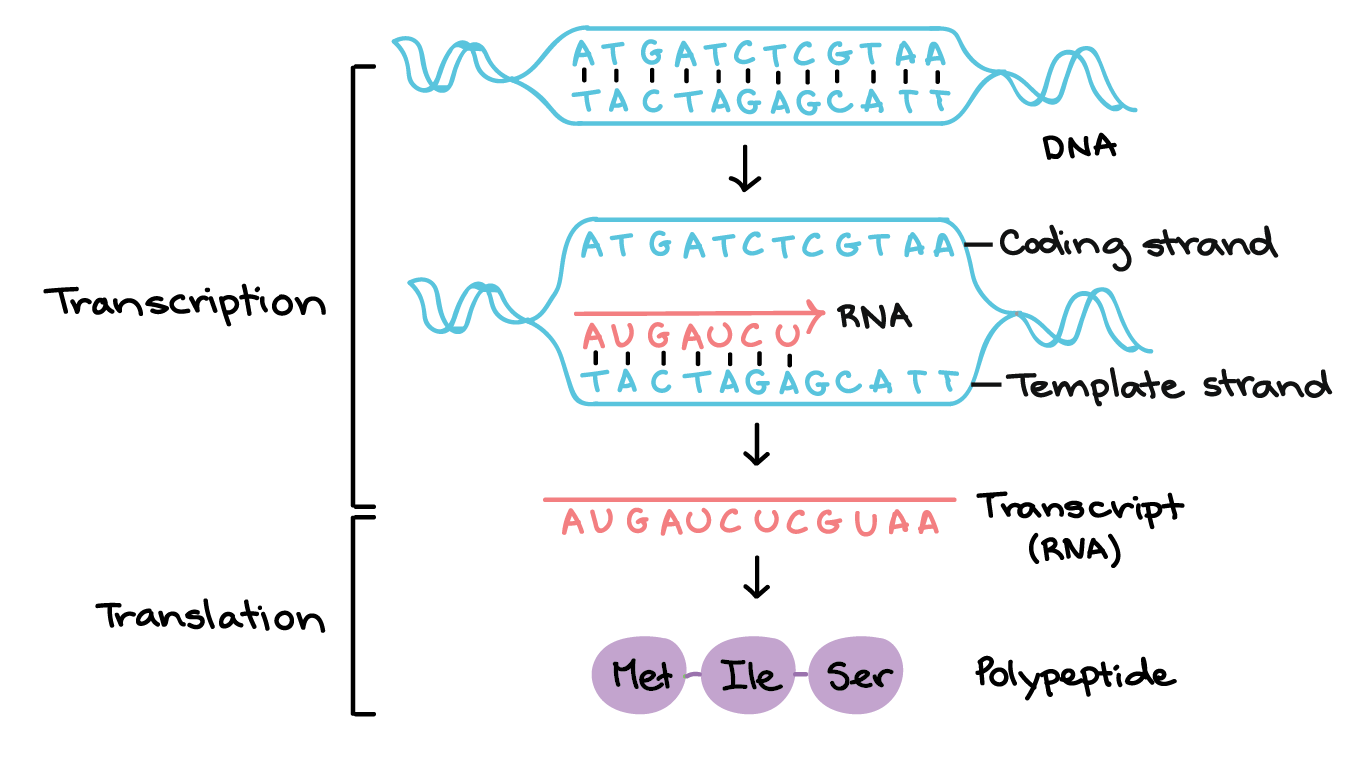
Stages Of Transcription Initiation Elongation Termination Article Khan Academy

Life Dna Rna And Protein Britannica

Automated Sequencing An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
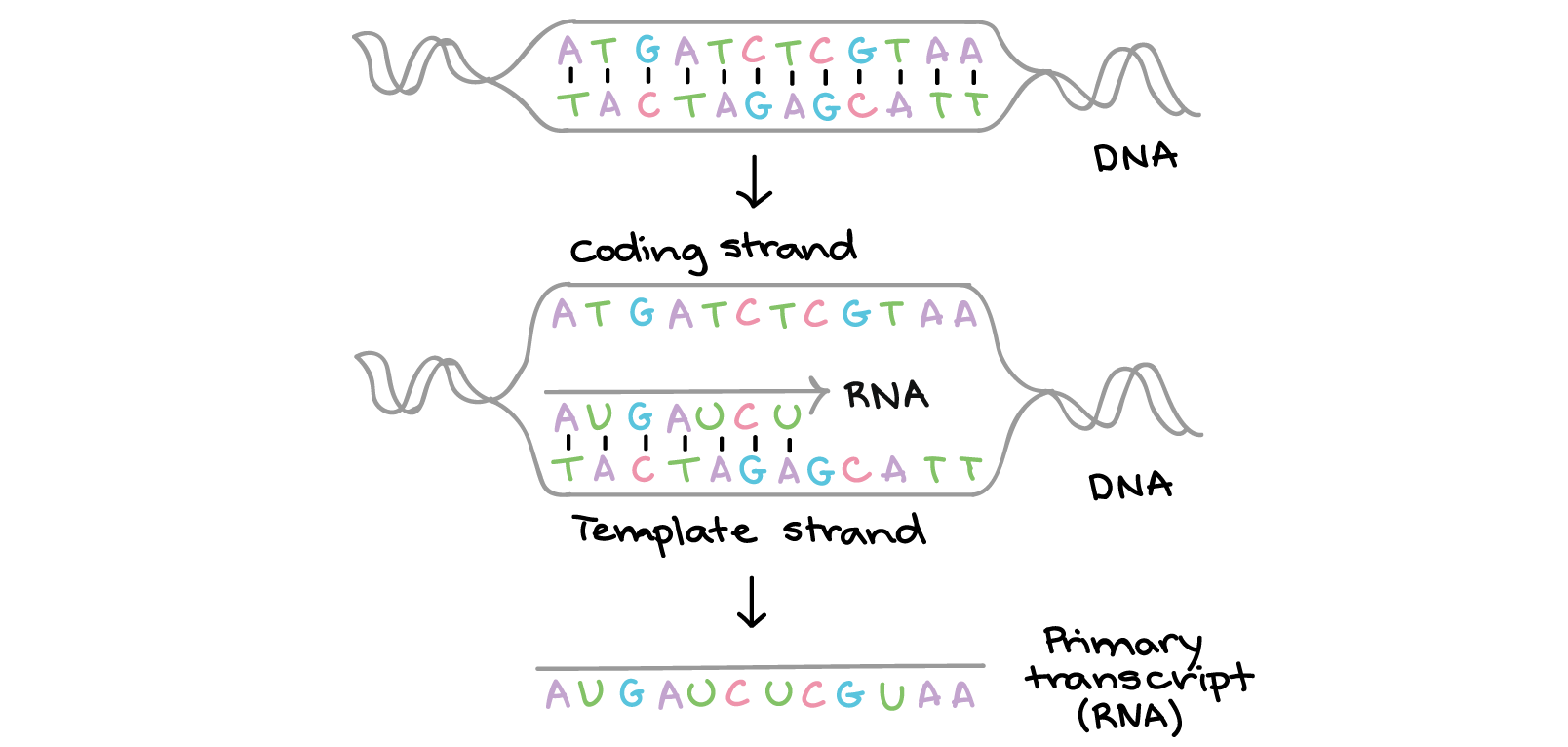
Intro To Gene Expression Central Dogma Article Khan Academy

Sanger Sequencing Steps Method

Life Dna Rna And Protein Britannica

6 Questions About Dna Answered Britannica
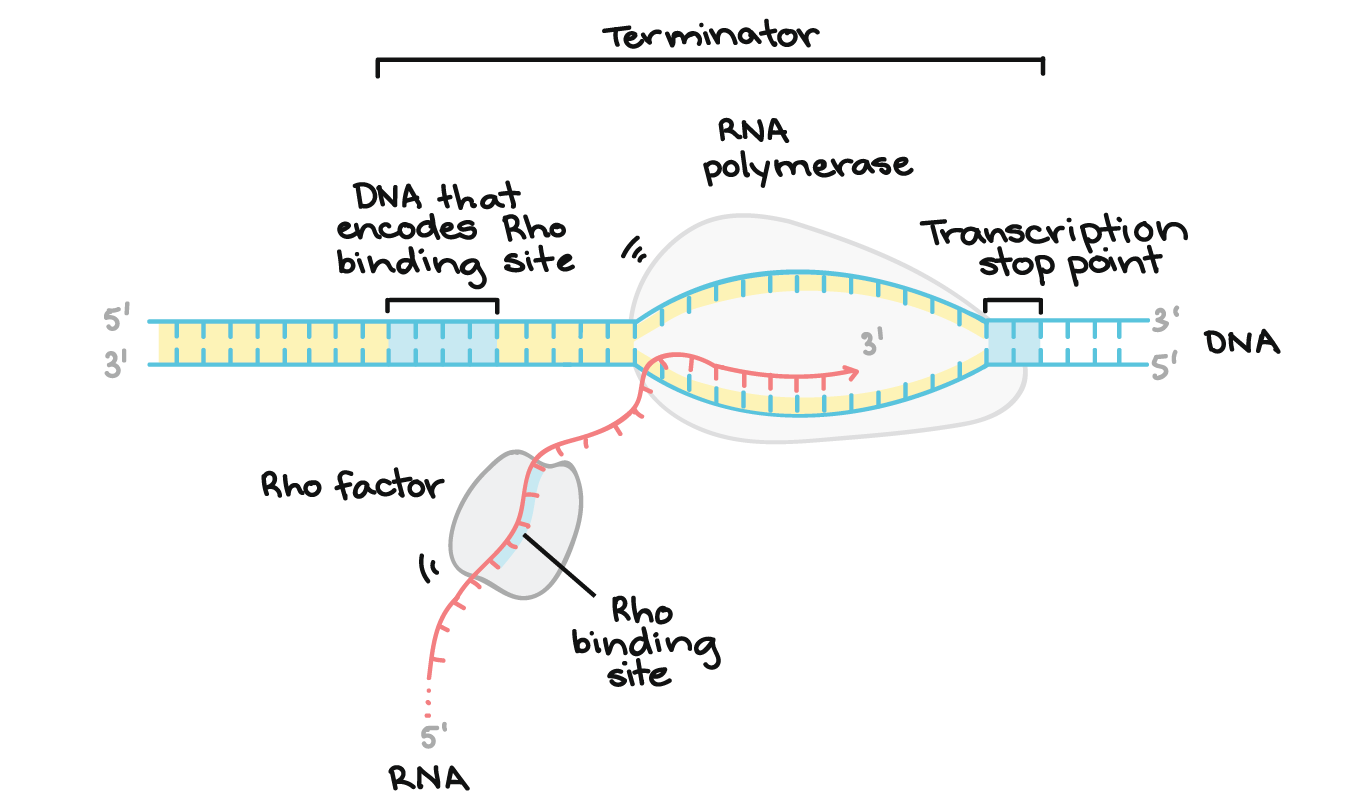
Stages Of Transcription Initiation Elongation Termination Article Khan Academy
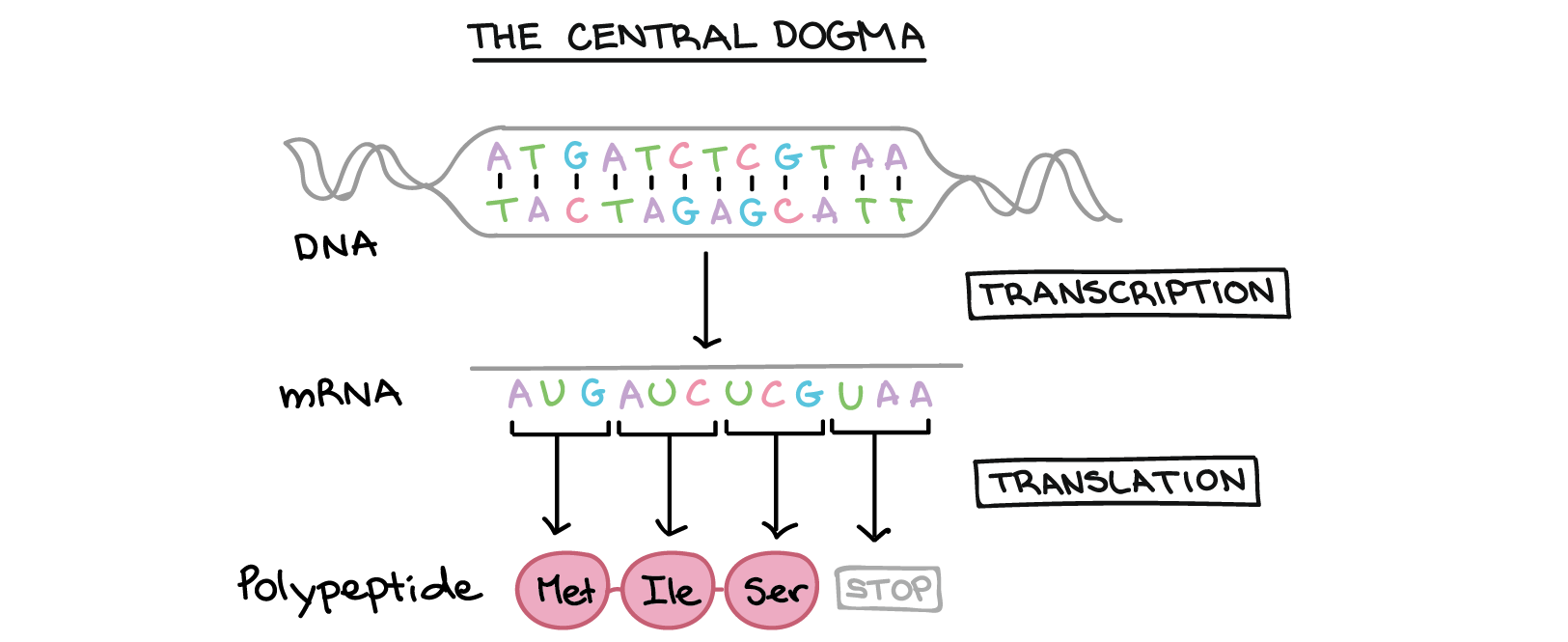
Intro To Gene Expression Central Dogma Article Khan Academy

Heredity The Genetic Code Britannica
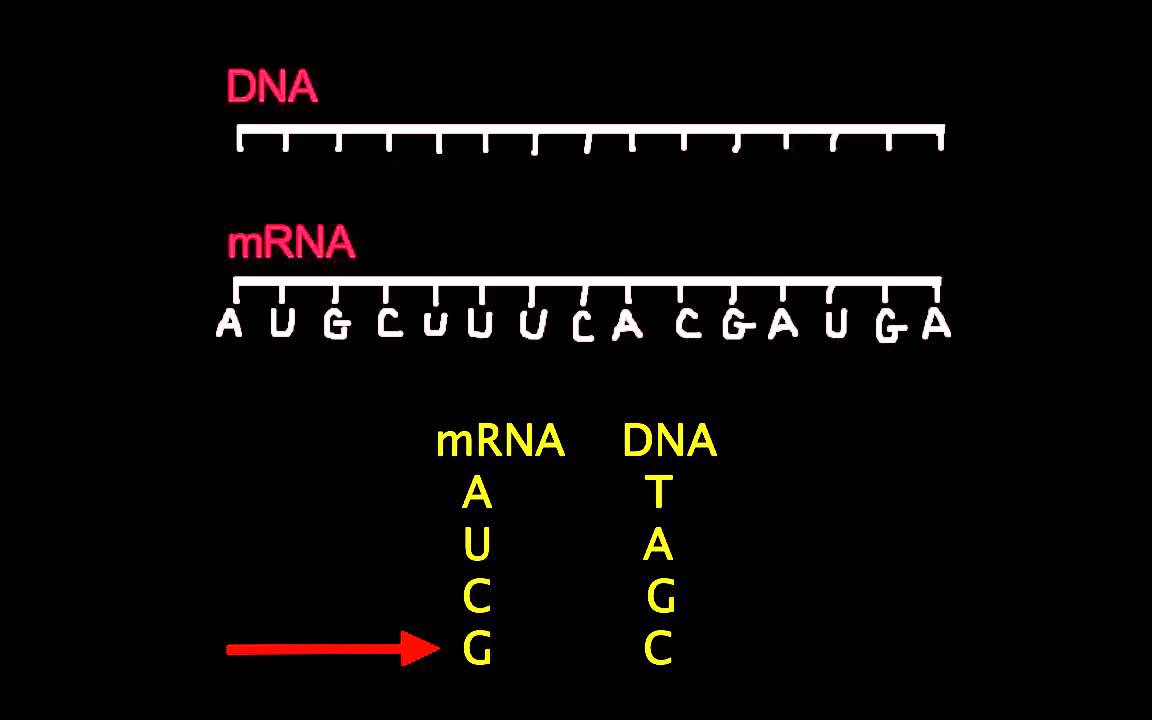
Topic 2 7 Dna Replication Transcription And Translation Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green
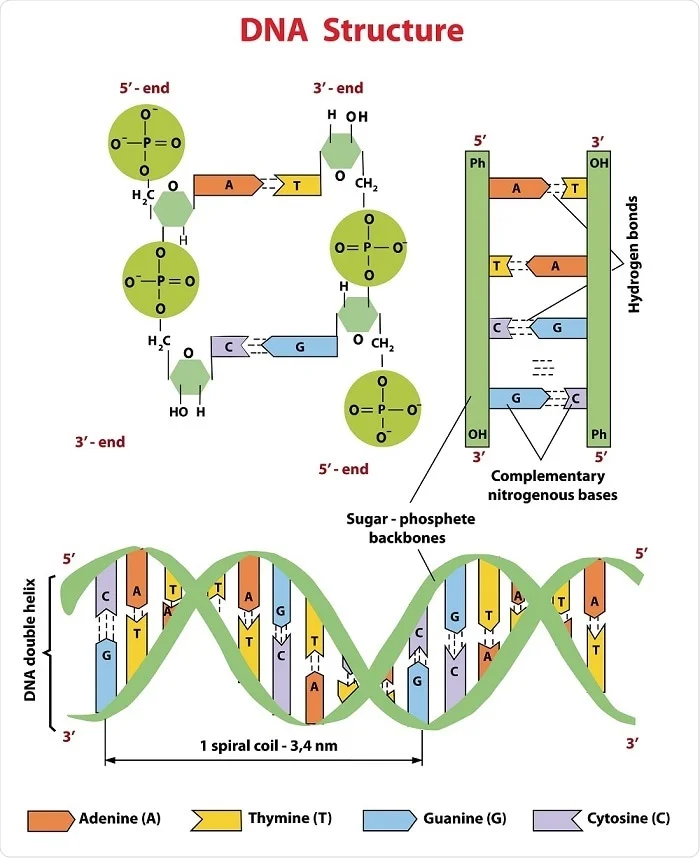
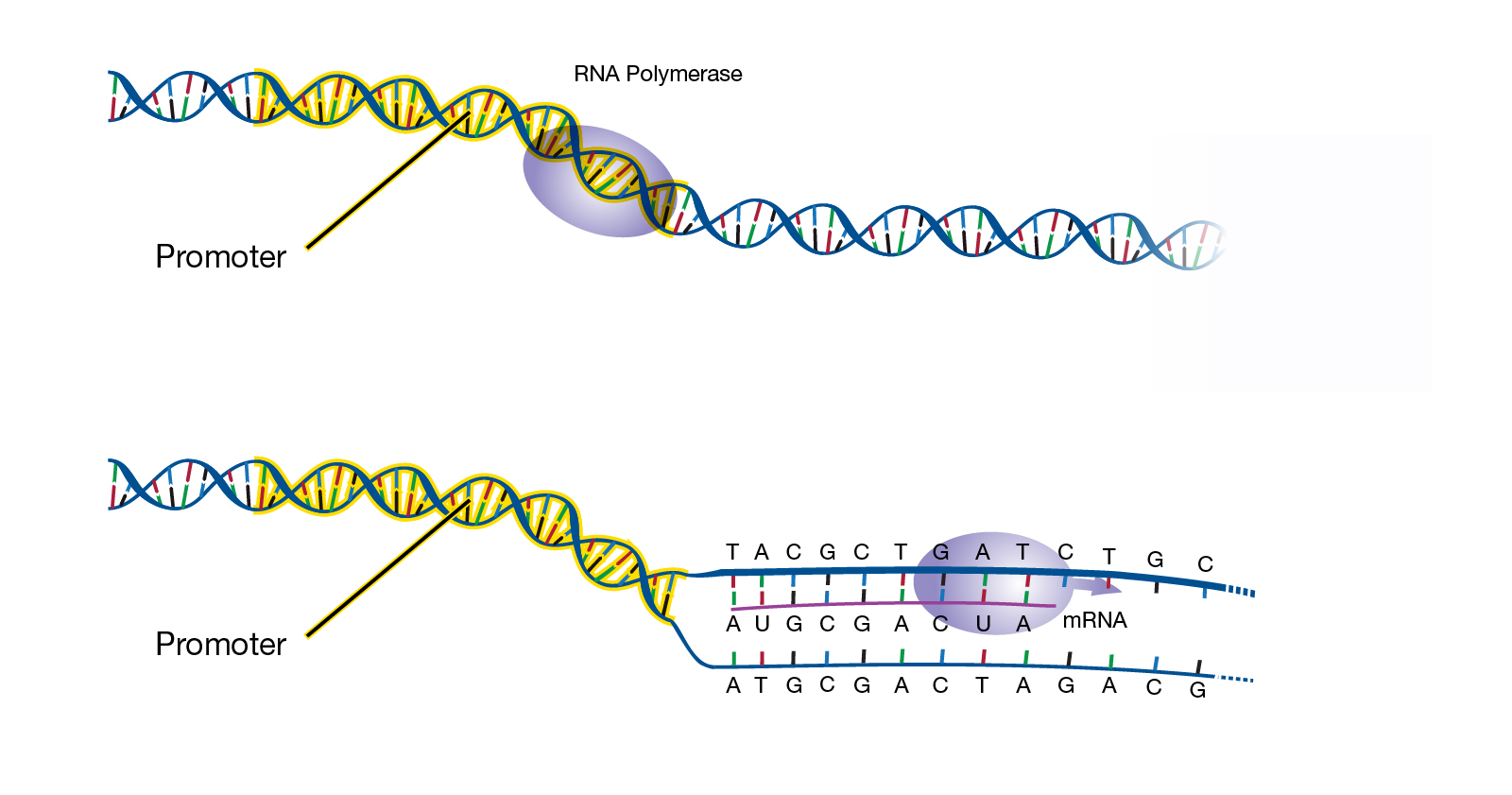

Comments
Post a Comment